Conditional FDA Approval: Understanding The Novavax COVID-19 Vaccine's Limitations
Welcome to your ultimate source for breaking news, trending updates, and in-depth stories from around the world. Whether it's politics, technology, entertainment, sports, or lifestyle, we bring you real-time updates that keep you informed and ahead of the curve.
Our team works tirelessly to ensure you never miss a moment. From the latest developments in global events to the most talked-about topics on social media, our news platform is designed to deliver accurate and timely information, all in one place.
Stay in the know and join thousands of readers who trust us for reliable, up-to-date content. Explore our expertly curated articles and dive deeper into the stories that matter to you. Visit Best Website now and be part of the conversation. Don't miss out on the headlines that shape our world!
Table of Contents
Conditional FDA Approval: Understanding the Novavax COVID-19 Vaccine's Limitations
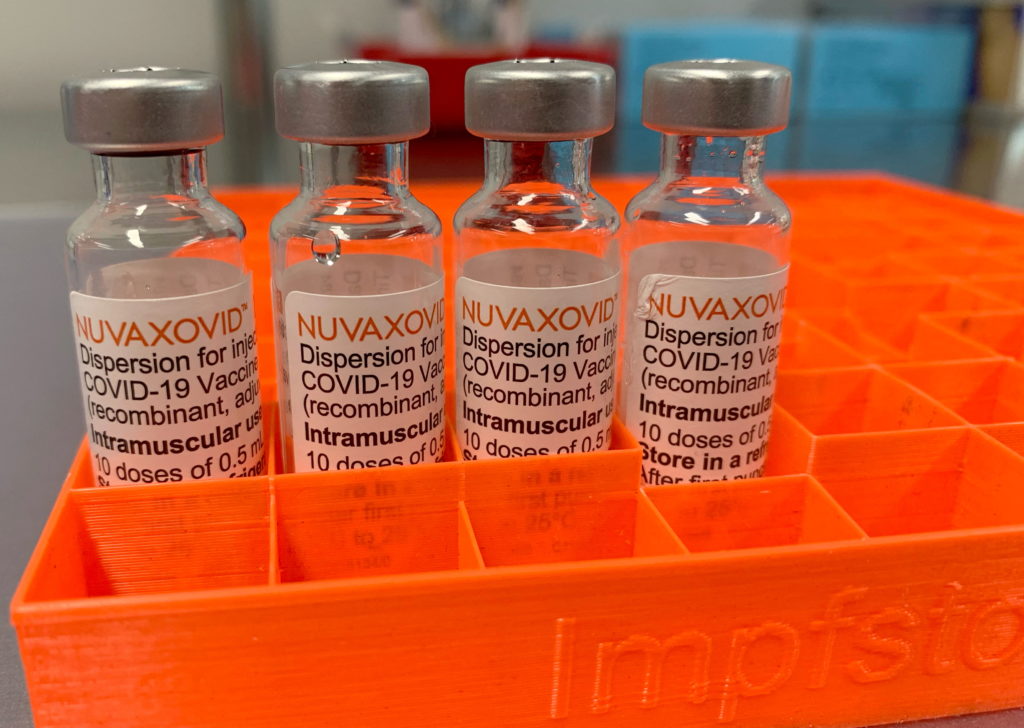
The Novavax COVID-19 vaccine, Nuvaxovid, finally received conditional FDA approval in July 2023, offering an alternative to mRNA vaccines for those hesitant about that technology. However, this approval comes with important caveats. Understanding the limitations of the Novavax vaccine is crucial for informed decision-making. This article will delve into the specifics of the conditional approval and highlight the areas where Nuvaxovid differs from its mRNA counterparts.
What is Conditional FDA Approval?
Unlike a full FDA approval, which signifies extensive and conclusive evidence of safety and efficacy, conditional approval allows for the quicker authorization of a vaccine during public health emergencies. This pathway requires the manufacturer to continue collecting data and fulfilling post-market requirements to confirm the vaccine's long-term safety and effectiveness. Essentially, the FDA grants conditional approval acknowledging the vaccine's potential benefits outweigh the known risks at that time, with ongoing monitoring crucial for maintaining approval.
Novavax Vaccine: A Different Approach
Nuvaxovid employs a different technology compared to Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines. It's a protein subunit vaccine, using lab-grown pieces of the virus's spike protein to trigger an immune response. This protein-based approach has been used for decades in other vaccines, potentially appealing to individuals wary of the newer mRNA technology.
Limitations of the Novavax Vaccine:
While offering a different technology, Nuvaxovid faces some limitations:
-
Lower Efficacy: Clinical trials showed lower efficacy compared to mRNA vaccines, particularly against emerging variants. This doesn't necessarily mean it's ineffective; it simply means its protective effect might be less robust. Further research is needed to understand its long-term protection against various variants.
-
Slightly Higher Side Effects: Although generally well-tolerated, some individuals experienced slightly higher rates of certain side effects, such as injection site pain and fatigue, compared to some placebo groups in clinical trials. However, these side effects were typically mild and transient.
-
Limited Real-World Data: Because it received authorization later than mRNA vaccines, there's less real-world data on its effectiveness and long-term safety. Ongoing monitoring is essential to gather this crucial information.
-
Logistical Challenges: The Novavax vaccine requires specific storage and handling conditions, potentially posing logistical challenges in certain settings compared to the more temperature-stable mRNA vaccines.
Who Might Benefit from the Novavax Vaccine?
Despite its limitations, the Novavax vaccine could benefit specific populations:
- Individuals hesitant about mRNA technology: The protein subunit approach may offer a preferred option for those concerned about mRNA vaccines.
- Specific clinical trials participants: Future studies may identify subgroups who experience greater benefit from the Novavax vaccine.
The Importance of Ongoing Monitoring:
The conditional approval highlights the FDA's ongoing commitment to monitoring the Novavax vaccine's safety and effectiveness. The manufacturer is required to provide additional data and meet specific requirements to maintain its authorization. This underscores the dynamic nature of vaccine development and the importance of continuous surveillance.
Conclusion:
The Novavax COVID-19 vaccine offers an alternative approach to COVID-19 prevention. However, it’s crucial to acknowledge its limitations regarding efficacy against certain variants and the need for ongoing monitoring. Individuals should consult their healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate vaccine based on their individual circumstances and health history. Staying informed about the latest research and updates on vaccine safety and efficacy is vital for informed decision-making regarding COVID-19 vaccination. For more information on vaccine safety and efficacy, consult the .

Thank you for visiting our website, your trusted source for the latest updates and in-depth coverage on Conditional FDA Approval: Understanding The Novavax COVID-19 Vaccine's Limitations. We're committed to keeping you informed with timely and accurate information to meet your curiosity and needs.
If you have any questions, suggestions, or feedback, we'd love to hear from you. Your insights are valuable to us and help us improve to serve you better. Feel free to reach out through our contact page.
Don't forget to bookmark our website and check back regularly for the latest headlines and trending topics. See you next time, and thank you for being part of our growing community!
Featured Posts
-
 Jenn Sterger Details Devastating Fallout From Brett Favre Sexting Scandal
May 20, 2025
Jenn Sterger Details Devastating Fallout From Brett Favre Sexting Scandal
May 20, 2025 -
 Tom Aspinall Vs Jon Jones The Controversy Behind Jones Recent Strip The Duck Statement
May 20, 2025
Tom Aspinall Vs Jon Jones The Controversy Behind Jones Recent Strip The Duck Statement
May 20, 2025 -
 The Return Of Star Wars Battlefront A Detailed Look
May 20, 2025
The Return Of Star Wars Battlefront A Detailed Look
May 20, 2025 -
 Investing In The Future The Economic And Societal Impact Of Us Medical And Scientific Research
May 20, 2025
Investing In The Future The Economic And Societal Impact Of Us Medical And Scientific Research
May 20, 2025 -
 How Climate Change Affects Pregnancy Outcomes And Fetal Development
May 20, 2025
How Climate Change Affects Pregnancy Outcomes And Fetal Development
May 20, 2025
